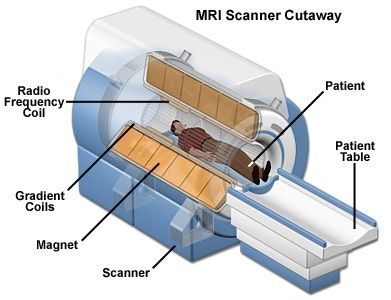
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic Resonance Imaging uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed images of the human anatomy. These images allow the radiologist to “see” soft tissue, such as muscles, fat and internal organs without the use of x-rays.
Because there is no ionizing radiation used in the exam, magnetic resonance imaging is a very popular tool in the medical community. In addition, the study is a totally painless exam and has no known side effects.
Capitol Imaging Services has a variety of systems in our arsenal of diagnostic technology. They include 3T ultra-high field, 1.5T high field, 1.2T high field open magnetic resonance imaging, and other open scanners. These systems meet nearly every need for a medical provider, specifically subspecialists such as orthopedic surgeons, neurologists, urologists, anesthesiologists and gastroenterologists who are most likely to recommend these studies for their patients.
When would this scan be ordered?
Typically, scans such as x-rays or perhaps an ultrasound are performed first. When these exams do not provide a diagnostic solution, magnetic resonance imaging is commonly warranted because there is a need to review more detailed images.
Health care professionals use these scans to diagnose a wide variety of conditions, from torn ligaments to tumors, to examining the brain and spinal cord.
If your provider wants to check solid tissues, like bone, a CT scan is likely the preferred choice. For example, your provider may order a CT scan to check for a bone break or fracture.
What Will I Experience?
Before the scan, Capitol Imaging Services will need to screen you to make sure it is safe to undergo the study. Some medical or electronic devices, such as implants, stents or certain pacemakers, may not be compatible with the scanners. Your safety is our top priority.
If you are determined to be unable to have an MRI, other types of diagnostic tests may be recommended as alternatives such as a CT or Ultrasound.
magnetic resonance imaging exams are painless. However, some patients find it challenging to remain still. Others may feel closed-in (claustrophobia) or anxious while in a conventional closed scanner. The scanner can be noisy. Nervous or anxious patients may be offered a mild sedative.
A patient may also ask their medical provider to prescribe a mild sedative to take before the exam. If a mild sedative is taken, the patient will need to have someone drive them to our center and take them home once the exam is done.
It is normal for the area of your body being imaged to feel slightly warm. It is important that you remain perfectly still while the images are being recorded, which is typically only a few seconds to a few minutes at a time. You will know when images are being recorded because you will hear tapping or thumping sounds when the coils that generate the radiofrequency pulses are activated. You will be able to relax between imaging sequences, but will be asked to maintain your position as much as possible.
You will usually be alone in the exam room during the procedure. However, the technologist will be able to see, hear and speak with you at all times using a two-way intercom.
You will be offered earplugs or a headset to reduce the noise of the scan, which produces loud thumping and humming noises during imaging. Our scanners are air-conditioned and well-lit. Some of our scanners have music you can listen to during the test.
If you have an exam that requires an injection of intravenous contrast material, it is normal to feel coolness and a flushing sensation for a minute or two following the injection. The intravenous needle may cause you some discomfort when it is inserted and once it is removed, you may experience some bruising. There is also a very small chance of irritation of your skin at the site of the IV tube insertion.
The length of time for an exam will vary. Typically, most scans will last 30 to 60 minutes.